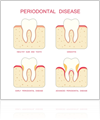
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is caused by poor dental hygiene. When plaque builds up on your teeth and hardens into tartar, it harbors harmful, dangerous bacteria. If not treated by a dentist or periodontist, this bacteria eventually causes gum disease. If you’re concerned that you might be suffering from gum disease in Bel Air , visit a dentist near you for treatment as soon as possible. Keep reading for information about why it’s important to treat gum disease.
Avoid Receding Gums 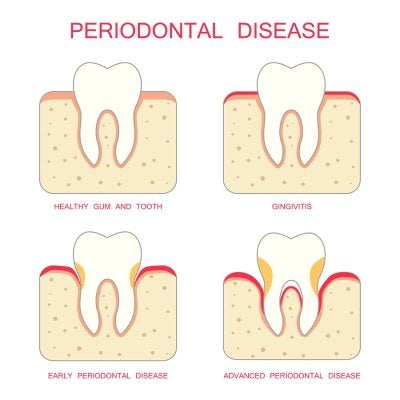 If left untreated, the early, milder symptoms of gum disease will quickly progress into much more serious dental problems. Gum disease causes your gums to become inflamed, tender, and red. They will bleed easily, making you very susceptible to oral infections. Your gums will also begin to recede. If you visit a dentist regularly, or visit a periodontist at the first sign of gum disease, you can avoid developing receding gums.
If left untreated, the early, milder symptoms of gum disease will quickly progress into much more serious dental problems. Gum disease causes your gums to become inflamed, tender, and red. They will bleed easily, making you very susceptible to oral infections. Your gums will also begin to recede. If you visit a dentist regularly, or visit a periodontist at the first sign of gum disease, you can avoid developing receding gums.
Prevent Tooth Loss
As gum disease continues to infect your gums and tissues, the gums will begin to pull away from the teeth. This causes spaces, or pockets, to form between the teeth and gums. These pockets are very vulnerable to infection, as it’s easy for bacteria and food to get trapped inside them. While the body’s immune system fights the bacterial infection, the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place will begin to break down. If an emergency dentist or periodontist doesn’t intervene, you may eventually suffer from tooth loss.
Decrease Your Risk of Developing Other Health Problems
The longer gum disease is left untreated, the more severe it becomes. Because it’s a very serious infection, it can spread to other parts of your body through your bloodstream. Your immune system will continue trying to fight the infection, which will tax your body’s resources, making you feel weak. If a dentist doesn’t treat gum disease, the infection can increase your risk of developing very serious health problems. Due to your weakened immune system, you will be much more susceptible to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disease, and certain types of cancer.